Definition:
Price elasticity of demand (PED) quantifies how the quantity demanded of a product changes in response to price variations.
Formula:
The formula for calculating price elasticity is:
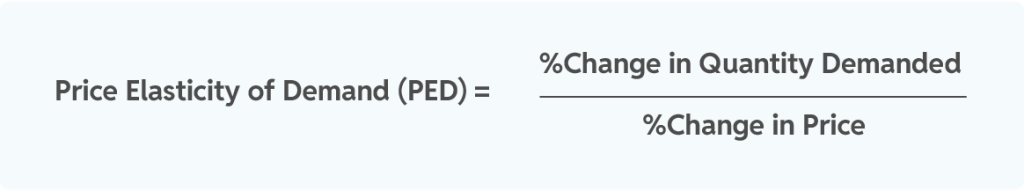
- If |PED| > 1, the product is elastic, meaning sales drop significantly with a price increase.
- If |PED| < 1, the product is inelastic, indicating that demand remains relatively stable despite price changes.
The importance of understanding price elasticity
Understanding price elasticity is vital for retailers as it provides insights into how changes in price can affect consumer demand in the retail market. This knowledge enables retailers to:
- Develop pricing strategies that resonate with their target audience.
- Predict consumer reactions to discounts and price increases.
- Maximize revenue and optimize profit margins.
Moreover, a strong grasp of price elasticity helps retailers:
- Identify opportunities for strategic promotions.
- Improve inventory management.
- Enhance competitiveness in the retail market.